Root Cause Analysis is the well-structured process to identify the root cause of the problem and not just its symptoms. Thus, RCA goes deeper in answering “why” to find out the very core issue that has been causing problems in an organization to resurface.
Such proactive mode of resolution makes sure to fix problems for present and future challenges, hence acting as a magic wand for effective problem solving.
Ever feel like you’re running in circles, constantly putting out fires at work? Well, now imagine how you can turn that chaos into pure clarity with a powerful new tool that goes deep into the mire of your issues. Uncover how root cause analysis can change your approach to solving your biggest issues and help your organization advance!
The Nitty-Gritty of Root Cause Analysis
What is Root Cause Analysis: More Than Just Problem-Solving
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a process that aims at addressing the overall cause of the problem rather than its symptoms. The best way to think of RCA is like detective work: it’s about inspecting the issues like a crime scene, where you not only see the damage but further investigate what might have brought about that damage. Persistently asking “why,” RCA peels away layers of a problem, revealing the contributing factors. All this pertains to a proactive methodology that empowers organizations to implement long-term solutions and enhance efficiency and effectiveness.
Why RCA Matters: Real-World Examples That’ll Make You Go “Aha!”
The importance of RCA can be gauged by the consideration of its impact on real-world scenarios. For instance, take the 1999 Mars Climate Orbiter mishap when NASA lost a $125 million spacecraft because of a mere unit conversion error.
Had the RCA been followed through effectively, it would have detected the miscommunication between teams at an early stage and probably could have saved millions and also saved the setback in space exploration.
Another good example is the Toyota sticky pedal crisis, running from 2009 to 2011, with millions of vehicles being recalled. Earlier remedies were directed toward the floor mats and sticky pedals, but an RCA identified the malfunction as originating from a software glitch in the electronic throttle control system.
Such knowledge not just addressed the problem at hand, but also started an almost revolution-like change in how safety was conducted in the car industry.
Take, for example, the Miracle on the Hudson: With years of groundwork on aviation RCA, Sully Sullenberger was able to land the US Airways Flight 1549 in the Hudson River in 2009, paving a way for better training of pilots, aircraft designs, and emergency response procedures. This example aligns RCA not only with solving problems but as an important tool for disaster prevention and advancing safety.
These are real-world examples of how RCA saves not only money and time but lives too. By identifying the root causes, an organization is empowered with a changed approach to challenges, creates a culture of improvement, and assures that problems don’t arise again. Embracing RCA means one is investing in long-term success and operational excellence.
The RCA Process: Rolling Up Your Sleeves and Getting to Work

It is extremely vital that every issue that is impacting an organization be addressed by identifying and pinning down the root cause for corrective action. The team can effectively solve issues and prevent recurrence by using a structured RCA process. Now, let’s proceed to understand the RCA process step by step.
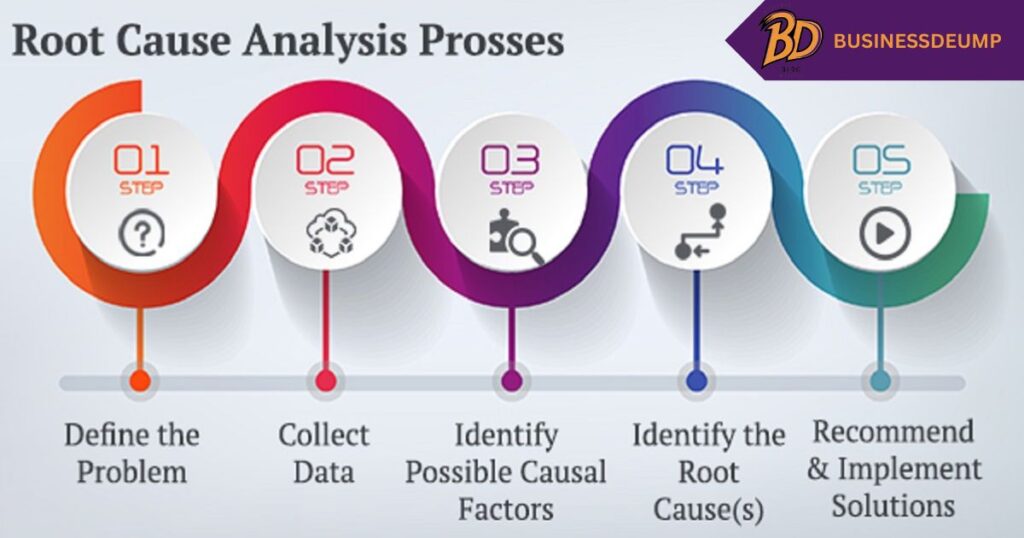
Step 1: Houston, We Have a Problem Identifying the Issue:
Identifying the problem is the first step in dealing with the RCA. The only way an effective analysis gets set on its way is through spelling out a clear statement of the problem in place. Here is how you nail this part of the process:
- Be specific: State clearly what the issue is. For example, say “Sales for Product X have been down by 20% in the last quarter” instead of just saying “Our sales are down.”
- Use Data: Back up your statement with data. Provide numbers, trends, and any other information to show the magnitude of the problem.
- Consider Impact: Think about the effect on business, employee and customer.
A well-stated problem lays a strong foundation for the next steps to be followed in the process of RCA.
Step 2: Gather Intel Like a Pro Detective:
Information Gathering: Once the problem has been identified, that is the time information has to be gathered. This implies data gathering and insight to shed light on the situation.
Cast a Wide Net: Data sources can take the form of:
- Production logs
- Interviews with employees
- Customer feedback
Be Objective: Focus on facts, not opinions. At the time the facts are incomplete, avoid jumping to conclusions.
Develop a Timeline: Record when the problem began and any changes or events that might relate to the buildup of the issue. This might put to notice a pattern.
Use of a data collection checklist can make sure that you don’t miss out on any useful information in your data to be collected.
Step 3: Searching for Potential Causes
Now, with the data, generate a list of potential causes of the problem. This stage is a marriage of creativity and analysis in terms of thinking about all possible causes.
Brainstorming Sessions: Engage your team in brainstorming sessions. Keep the discussion open so that everybody can contribute ideas, including even those that sound illogical.
Fishbone Diagram: This is a tool to help you identify and group the possible causes. Major categories that will be considered include:
- People
- Processes
- Equipment
- Environment
5 Whys Technique: At every possible cause, ask “why.” This will bring you down to deeper levels.
What you want to do here is come up with a comprehensive list of all the probable root causes that need further investigation.
Step 4: Eureka! Pinpointing the Root Cause
Now that you have a list of possible causes, it is the time to analyze and find out which is the root cause of the problem.
- Analyze the Information: Trends, patterns, correlations look for relationships in the data you have gathered.
- Test Your Hypotheses: If feasible, test your theories of what could be wrong by experimentation or simulation.
- Use Logic and Critical Thinking: Many a time you’ll use dots to connect with creative thinking. Assimilate all the information on hand to reach informed conclusions.
For instance, if there are frequent breakdowns of machinery at a manufacturing plant, determine whether current changes in either raw materials or procedures might be the cause.
Step 5: Time to Fix This Mess Implementing Solutions
Having identified the root cause, the time has come to implement solutions that will keep the problem from occurring again in the future.
- Address the Root Cause: Solutions to be administered should therefore focus on what would effectively handle the root cause of the problem, rather than treatment of symptoms.
- Brainstorm Multiple Solutions: Jot down at least two or three ways in which you can solve this problem. Review how feasible and impactful they are.
- Engage Stakeholders: Involve all relevant people in making the decision, especially employees affected by the solution.
- Action Plan: Detail who needs to do what and by when in implementing the solution
A well-laid out action plan provides accountability and a way forward.
Step 6: Did We Nail It? (Checking for Effectiveness)
The last step in the RCA process is to validate if the implemented solutions have indeed solved the problem.
- Track Your Key Metrics: Track the key indicators that have been influenced because of the original problem. Check if these metrics have changed for good after the solutions are implemented.
- Gather Feedback: Be it from your employees or customers, get feedback regarding any changes. Indeed, their contribution can make you aware of reams of information associated with whether your solutions are good or bad.
- Be patient: sometimes, solutions take time before results are realized. Do not easily rush into judgment.
RCA Tools: Your Problem-Solving Swiss Army Knife

The organizations perform an important process of identifying and eliminating the root cause of problems. There are several tools that can be used to facilitate effective root cause analysis and make the performance of the analysis much easier in finding the real cause of the problem.
We will discuss four of the essential root cause analysis tools in this paper: Fishbone Diagram, 5 Whys Technique, Fault Tree Analysis, and Failure Mode and Effects Analysis. Each tool has its own amazing strengths that are able to elevate and boost problem solving skills.
The Fishbone Diagram: Not Your Average Fish Tale
The Fishbone Diagram is also often called the cause and effect diagram or the Ishikawa Diagram. It is a visual tool that helps teams by structuring potential causes of a problem. This is an easier way to distinguish and analyze the various factors that cause a problem.
Key Features of the Fishbone Diagram
- Visual Display: It is in the shape of a fish skeleton, where the problem is at the “head” and causes generate from it in a branching format, resembling “bones.” This visual format helps to structure ideas and foster brainstorming.
- Categorization: The most common categories include
- People: Human factors that could be contributing to the problem.
- Processes: Inefficiencies or flaws in workflows.
- Equipment: Problems with machinery or tools.
- Environment: Things outside the immediate control of the process or team that could be driving performance.
How to Create a Fishbone Diagram:
Define Problem : State the problem at the top of the diagram.
Identify Major Categories : Draw branches for each major category of possible causes.
Brainstorm Specific Causes : Under each category, list specific factors that may contribute to the problem.
Analyse and Discuss : As a team, review this diagram identifying which causes should be investigated further.
Benefits :
- Allows the team to discuss and come up with ideas.
- Provides an overall picture of probable causes.
- It helps to identify areas requiring further study.
5 Whys Technique: Bring Out Your Inner Toddler
The 5 Whys Technique is a really simple yet highly effective tool where the process is all about continuous asking asking “why” over and over again, in order to get to the root of an issue. This tool helps unravel insights that would otherwise be kept underneath the surface.
Key Features of the 5 Whys Technique:
- Ease: You have to ask “why” a number of times, for example five, in order to reach the most basic cause.
- Focus on Causes: The approach shifts the focus from the symptoms to listing underlying problems; thus it gives a significant impact on the understanding of the problem.
How to Apply the 5 Whys Technique
Define the Problem: Make a clear description of the issue that you want to resolve.
For each Response,
Ask Why: For each response given, it is important to ask why the problem exists. Document the question asked.
Keep Iterating: For each question after the first, ask why, until you get to the root cause. As a general rule, this should happen five times; however, it could be more or less.
Document Findings: Record every answer and see the tree grow until the root of the problem.
Benefits:
- Finds hidden root causes not obvious on the surface.
- Builds critical thinking and deep analysis.
- Eliminates skinny solutions by focusing on real issues.
Fault Tree Analysis: It’s Not About Blaming Trees
Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) is a top-down, deductive approach to failure represented in terms of relationship with its possible causes of failure. It mainly finds applications in situations involving the combination of several factors or events that cause a problematic issue in complex systems.
Key Features of Fault Tree Analysis:
- Visual Display: FTA is visually presented using a diagram shaped like a tree for defining the failures and their causes, whereby it starts from a point being the top event (the problem) and evolving from there to a low or basic event.
- Logical Relationships: The diagramming uses logic gates, AND and OR, for indicating the various causes or events that combine to cause the top event.
Performing Fault Tree Analysis:
- Determine the Top Event: Define or designate an undesired event or failure you are seeking to analyze:.
- Identify Intermediate Events: Decompose the top event into the intermediate events that are the contributors to the top event.
- Identify Basic Events: Further decompose these intermediate events if still possible until you reach basic events that can not be decomposed any further.
- Apply Logic Gates: Utilize AND and OR gates that indicate how different events are combined that cause the top event.
- Analyzing the Tree: The fault tree that results is analyzed to determine possible root causes.
Advantages:
Especially for the system that is more complicated where more factors are involved in the interaction.
It offers a structured approach to identifying and recognizing failure mechanisms.
It can identify multiple causes and cause-and-effect relationships.
FMEA: Insights for the Future (Sort of)
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) is the forward-looking process that uncovers the weak links in a process or product long before the failures occur. The ‘team’ approach does this through determining the likelihood and impact of such failures, making recommendations, and recording indisputable results.
Key Points in an FMEA :
- Proactive Technique: it is the proactive technique and more concern is towards fore sighting the problems, not just avoiding the problems after execution.
- Assessment of Risk: ranking of each failure mode on the basis of severity, occurrence and detection
How to do FMEA
- BusinessAudit the Potential Failure Mode : make of al list of all the possible ways by which a process or products could fail.
- Identify Effects: estimate the potential effect of the failure mode on process, product or customer.
- During this process, the following ratings need to be assigned for every failure mode:
- Severity: How severe would be the effect? (1-10 scale)
- Occurrence: How likely is the failure to happen? (1-10 scale)
- Detection: How easily can the failure be detected? (1-10 scale)
- Calculate Risk Priority Number: Multiply the ratings for severity, occurrence, and detection to arrive at the RPN of each of the failure modes.
- Prioritize Actions: Arranging the RPN will allow prioritization of which of the failure modes need immediate actions.
Benefits:
- Identifies and assists organizations proactive in possible problems.
- It ensures effective management of risks and decision-making.
- Enhances the quality of products and process reliability.
(RCA) is a powerful problem solving method that can help organizations identify and address underlying issues. However, this process is not without its challenges. Teams may encounter hurdles that can hinder their ability to effectively analyze problems and implement solutions. In this article, we’ll explore three common challenges faced during RCA time constraints, data overload, and the blame game and provide strategies for overcoming these obstacles.
Time Crunch: RCA Ain’t No Speed Dating
When a problem arises, the pressure to find a quick solution can be overwhelming. However, This is a methodical process that requires time and careful consideration. Rushing through RCA often leads to superficial fixes instead of addressing the root cause, which can result in recurring issues down the line.
Strategies to Overcome Time Constraints:
- Implement Temporary Fixes: If immediate action is necessary, consider implementing a short-term solution to mitigate the problem while conducting a thorough RCA. This helps stabilize the situation without sacrificing the depth of the analysis.
- Set Realistic Timelines: Communicate clearly with stakeholders about the time required for an effective RCA. Setting realistic expectations ensures that everyone understands the need for a thorough investigation.
- Prioritize RCA Efforts: Not all problems require an extensive RCA. Prioritize which issues warrant a deep dive and which can be addressed with simpler solutions. Focus your resources on high-impact problems that affect safety, quality, or customer satisfaction.
- Delegate Responsibilities: Distribute tasks among team members to speed up the process. By leveraging the strengths and expertise of various team members, you can streamline data collection, analysis, and solution implementation.
Data Overload: Drowning in Information? Here’s Your Life Vest

In today’s data-driven environment, teams often find themselves overwhelmed by the sheer volume of information available. This can make it challenging to discern relevant data from noise, complicating the RCA process.
Strategies to Manage Data Overload:
- Define Relevant Metrics: Clearly outline which data points are relevant to the problem at hand. Focus on metrics that directly correlate with the issue to prevent unnecessary data collection.
- Use Data Visualization Tools: Utilize charts, graphs, and diagrams to simplify complex data sets. Visual aids can help teams quickly identify trends, patterns, and anomalies, making it easier to analyze information.
- Leverage Technology: Consider using RCA software or data analytics platforms to organize and analyze data efficiently. Tools like Tableau or Power BI can help you sift through vast amounts of information and extract actionable insights.
- Conduct a Preliminary Analysis: Before diving into a full RCA, perform a preliminary analysis to narrow down potential causes. This approach helps focus your efforts on the most relevant data and can reduce the overwhelming feeling of data overload.
READ MORE POST : Dnd Size Chart: A Game-Changer for Your Adventures
The Blame Game: How to Avoid Pointing Fingers
One of the most significant challenges in conducting RCA is the tendency for team members to shift blame onto others. This can create a toxic environment that stifles open communication and hinders collaboration.
Strategies to Foster a Constructive Environment:
- Promote a Culture of Learning: Emphasize that RCA is about understanding processes and systems, not assigning blame. Encourage team members to view problems as opportunities for improvement rather than failures.
- Focus on Processes, Not People: Shift the conversation from individual actions to the systems and processes that may have contributed to the issue. This approach helps identify weaknesses in procedures that need to be addressed.
- Encourage Open Communication: Create a safe environment where team members feel comfortable sharing their thoughts and insights. Foster a culture of transparency where employees can discuss issues without fear of reprisal.
- Lead by Example: Leaders should model the behavior they wish to see in their teams. Acknowledge your own mistakes and demonstrate a commitment to learning from failures. When leaders admit their own shortcomings, it encourages others to do the same.
RCA Best Practices: Becoming a Root Cause Analysis Rockstar
To excel in Root Cause Analysis (RCA) and become a true problem-solving expert, you need to follow some best practices that will enhance your effectiveness and ensure lasting solutions. Here are three key areas to focus on: building your RCA dream team, creating a culture of continuous improvement, and leveraging technology with RCA tools for the digital age.
Building Your RCA Dream Team
RCA is a collaborative effort that benefits from diverse perspectives and expertise. Assembling the right team is crucial for a successful analysis. Here’s how to do it:
- Diverse Perspectives: Include team members from different departments and levels within the organization. Diverse viewpoints help in uncovering different aspects of a problem that might otherwise be overlooked.
- Subject Matter Experts (SMEs): Ensure that you have SMEs who have in-depth knowledge of the processes or systems involved. Their expertise is invaluable in accurately identifying root causes and effective solutions.
- Fresh Eyes: Sometimes, individuals who are not directly involved with the problem can offer fresh perspectives. Including team members who are unfamiliar with the process can lead to innovative solutions.
- Effective Communication: Choose team members who communicate well and can work collaboratively. Good communication ensures that all ideas and data are shared openly and considered.
- Leadership Support: Having the backing of senior management is essential. Their support can provide the necessary resources and authority to implement solutions effectively.
Creating a Culture of Continuous Improvement
For RCA to be truly effective, it must be embedded within a culture that values continuous improvement. Here’s how to foster such a culture:
- Training and Education: Provide regular training on RCA techniques and tools to all employees. This ensures that everyone understands the importance of RCA and knows how to contribute effectively.
- Encourage Reporting: Create an environment where employees feel safe to report problems and near-misses without fear of blame. Encourage them to view issues as opportunities for improvement.
- Celebrate Successes: Publicly acknowledge and celebrate successful RCA projects. Highlight how identifying and solving root causes has led to significant improvements in safety, efficiency, or customer satisfaction.
- Feedback Loops: Establish mechanisms for continuous feedback. Regularly review RCA processes and outcomes to learn from them and refine your approach.
- Integrate RCA into Processes: Make RCA a standard part of your organizational processes. For instance, include it in regular meetings, project planning, and performance reviews.
Leveraging Technology: RCA Tools for the Digital Age
Modern technology can significantly enhance the RCA process, making it more efficient and effective. Here are some key tools and technologies to leverage:
- RCA Software: Tools like Taproot® and Causelink® streamline the RCA process by providing structured frameworks for data collection, analysis, and reporting. These tools can help manage complex investigations and ensure that no step is overlooked.
- Data Analytics Platforms: Utilize platforms like Tableau or Power BI to analyze large datasets. These tools can help you identify patterns, trends, and correlations that might not be apparent through manual analysis.
- Collaboration Tools: Platforms like Slack or Microsoft Teams facilitate real-time communication and collaboration among RCA team members. These tools can help keep everyone on the same page and ensure timely sharing of information.
- Machine Learning and AI: Advanced technologies like machine learning and artificial intelligence can enhance RCA by predicting potential problems before they occur. These technologies analyze historical data to identify patterns and predict future issues, allowing for proactive measures.
- Visualization Tools: Use tools to create visual representations of data and processes, such as Fishbone Diagrams, Flowcharts, and Fault Trees. Visualization helps in understanding complex issues and communicating findings effectively.
The Future of Root Cause Analysis: Crystal Ball Not Included
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) has long been a cornerstone of problem–solving in various industries. As technology advances, the future of RCA promises even more powerful tools and methodologies to enhance our ability to identify and address the root causes of issues.
Two of the most exciting developments in this field are the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML), and the rise of Predictive RCA. Let’s explore how these innovations are transforming RCA.
AI and Machine Learning: The New Kids on the RCA Block
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are revolutionizing many aspects of our lives, and RCA is no exception. Here’s how these technologies are changing the game:
- Pattern Recognition: AI and ML excel at analyzing vast amounts of data to identify patterns that humans might miss. By examining historical data, these technologies can pinpoint subtle correlations and trends that could indicate underlying problems. This ability to recognize patterns helps in identifying root causes more quickly and accurately.
- Automated Data Analysis: One of the biggest challenges in RCA is sifting through large datasets to find relevant information. AI can automate this process, significantly reducing the time and effort required. Machine learning algorithms can be trained to filter out noise and highlight critical data points, making the analysis phase much more efficient.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP enables AI systems to understand and analyze text data from various sources, such as incident reports, maintenance logs, and customer feedback. This capability allows for a more comprehensive analysis by incorporating qualitative data, which is often rich in insights but difficult to process manually.
- Continuous Learning: Machine learning models can continuously improve over time as they are exposed to more data. This means that the more an organization uses AI for RCA, the better it gets at predicting and identifying root causes. This continuous learning loop enhances the accuracy and effectiveness of RCA efforts.
READ MORE POST : Plessner Coaching in lutherstraße 2 34327 körle
Predictive RCA: Solving Problems Before They Happen
Predictive RCA takes the traditional approach a step further by not just identifying root causes after problems occur, but by predicting and preventing them before they happen. Here’s how predictive RCA is shaping the future:
- Proactive Problem-Solving: Predictive RCA leverages historical data and advanced analytics to forecast potential issues. By identifying patterns and trends that precede failures, organizations can take proactive measures to prevent problems from occurring. This shift from reactive to proactive problem-solving can save significant time, money, and resources.
- Early Warning Systems: Predictive models can serve as early warning systems, alerting organizations to potential problems before they escalate. For example, in manufacturing, sensors can monitor equipment performance and send alerts when certain thresholds are breached, indicating that maintenance is needed. This helps in avoiding costly downtimes and ensuring smooth operations.
- Resource Optimization: By predicting where and when problems are likely to occur, organizations can allocate resources more effectively. Maintenance teams can prioritize tasks based on the likelihood of failure, ensuring that critical issues are addressed promptly while avoiding unnecessary maintenance on equipment that is functioning well.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Predictive RCA provides decision-makers with data-driven insights that enhance strategic planning. By understanding the factors that contribute to potential issues, leaders can make informed decisions about investments, process improvements, and risk management.
The Integration of AI, ML, and Predictive RCA
The true power of these technologies lies in their integration. When AI and ML are combined with predictive RCA, the result is a robust system that continuously monitors, analyzes, and improves organizational processes. Here’s what this integration looks like in practice:
- Real-Time Monitoring: AI-powered systems can monitor operations in real-time, providing continuous insights into performance and potential issues.
- Adaptive Models: Machine learning models can adapt to new data, refining their predictions and improving their accuracy over time.
- Comprehensive Analysis: By incorporating both quantitative data (sensor readings, production metrics) and qualitative data (text reports, customer feedback), these integrated systems provide a holistic view of organizational health.
- Scalability: These technologies can be scaled across various departments and locations, ensuring that the benefits of predictive RCA are realized throughout the organization.
Wrapping It Up: Your RCA Action Plan

Implementing a robust Root Cause Analysis (RCA) action plan can significantly enhance your organization’s problem solving capabilities. Here’s a concise guide to help you get started:
1. Understand the Basics
Root Cause Analysis is about identifying the fundamental cause of a problem, not just treating its symptoms. By addressing the root cause, you can prevent the issue from recurring, saving time, resources, and reducing frustration.
2. Follow a Structured Process
Implementing RCA requires a methodical approach. Here are the key steps:
- Define the Problem: Clearly articulate the issue. Be specific and use data to quantify the problem.
- Gather Data: Collect relevant information from various sources. Look at production logs, interview employees, and review customer complaints.
- Identify Possible Causes: Brainstorm potential causes using techniques like Fishbone Diagrams, the 5 Whys, and Fault Tree Analysis.
- Determine the Root Cause: Analyze the data and test your hypotheses to pinpoint the true cause.
- Implement Solutions: Develop and apply solutions that address the root cause, not just the symptoms.
- Verify Effectiveness: Monitor the outcomes to ensure the problem is resolved and doesn’t recur.
3. Build a Strong RCA Team
A successful RCA requires a diverse team with various perspectives and expertise. Include people from different departments and levels within the organization. This diversity helps in identifying different aspects of the problem and potential solutions.
4. Leverage Technology
Utilize modern tools to enhance your RCA process:
- RCA Software: Tools like Taproot® and Causelink® streamline data collection and analysis.
- Data Analytics Platforms: Use software like Tableau or Power BI for visual data analysis.
- Collaboration Tools: Platforms like Slack or Microsoft Teams facilitate communication and coordination among team members.
5. Create a Culture of Continuous Improvement
Incorporate RCA into your organization’s DNA:
- Training: Provide RCA training for employees at all levels to ensure everyone understands the process.
- Celebrate Successes: Share successful RCA outcomes to demonstrate its value and encourage its use.
- Learn from Near-Misses: Apply RCA to close calls as well as actual problems to proactively improve processes.
6. Monitor and Refine
RCA is an ongoing process. Continuously monitor the effectiveness of implemented solutions and refine your approach as needed. This continuous improvement mindset ensures long-term benefits and adaptability to new challenges.
Conclusion
Root Cause Analysis is a very powerful tool or strategy used to explore and research the key causes of repeated incidents within an organization. Induction of understanding the basic and its signalines and structure is important in the development of a preventive approach toward a solution of the constant problem and improvement. The full range of competency, application of the latest technology, and always getting better are the muscles important to maximize the effectiveness of strategies.
The application of the action plan on your part to your organization will introduce that element which will transform your organization into a very powerful one, as it relates to solving more problems with increasing outputs, thus saving more money and being successful. Adopt RCA into your operations and see your organization transform into being proactive and resilient enough to take on any challenge that it has before it. Dedication and a lot of practice will surely land you on rock star status when performing for your organization and consequently driving it toward a future of sustained excellence.
FAQs
What is the root cause analysis method of problem-solving?
- It identifies the fundamental cause of a problem to prevent recurrence.
What is the core of the root cause analysis?
- The core is finding and addressing the root cause, not just symptoms.
What is meant by root cause analysis?
- It’s a systematic approach to identifying the underlying cause of a problem.
What are the 5 steps of RCA?
- Define the problem, gather data, identify possible causes, determine the root cause, implement and verify solutions.